Testing with Windows Sandbox
Windows Sandbox provides an ideal environment for testing ImmyBot deployments and configurations in a safe, isolated container. This guide explains how to set up and use Windows Sandbox with ImmyBot.
What is Windows Sandbox?
Windows Sandbox is a lightweight desktop environment that:
- Creates a temporary, disposable instance of Windows
- Resets completely when closed, leaving no persistent state
- Provides isolation from your host system
- Starts up quickly and is optimized for testing
This makes it perfect for testing ImmyBot deployments without affecting your production environment.
Prerequisites
- Windows 10 Pro, Enterprise, or Education (version 1903 or later)
- Virtualization capabilities enabled in BIOS/UEFI
- At least 4GB of RAM (8GB recommended)
- At least 1GB of free disk space
Enabling Windows Sandbox
If you haven't used Windows Sandbox before, you need to enable it first:
- Open Windows PowerShell as Administrator
- Run the following command:
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -FeatureName "Containers-DisposableClientVM" -All -Online -NoRestart- Restart your computer if prompted
Alternatively, you can enable it through Windows Features:
- Open Control Panel > Programs > Turn Windows features on or off
- Check the box for "Windows Sandbox"
- Click OK and restart if prompted
Testing ImmyBot in Windows Sandbox
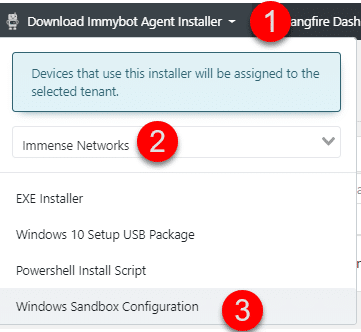
Step 1: Download the Windows Sandbox Configuration File
From the ImmyBot dashboard, download the Windows Sandbox configuration file (.wsb):
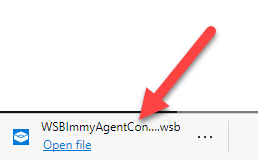
Step 2: Launch the Sandbox Environment
Double-click the downloaded .wsb file to launch Windows Sandbox:
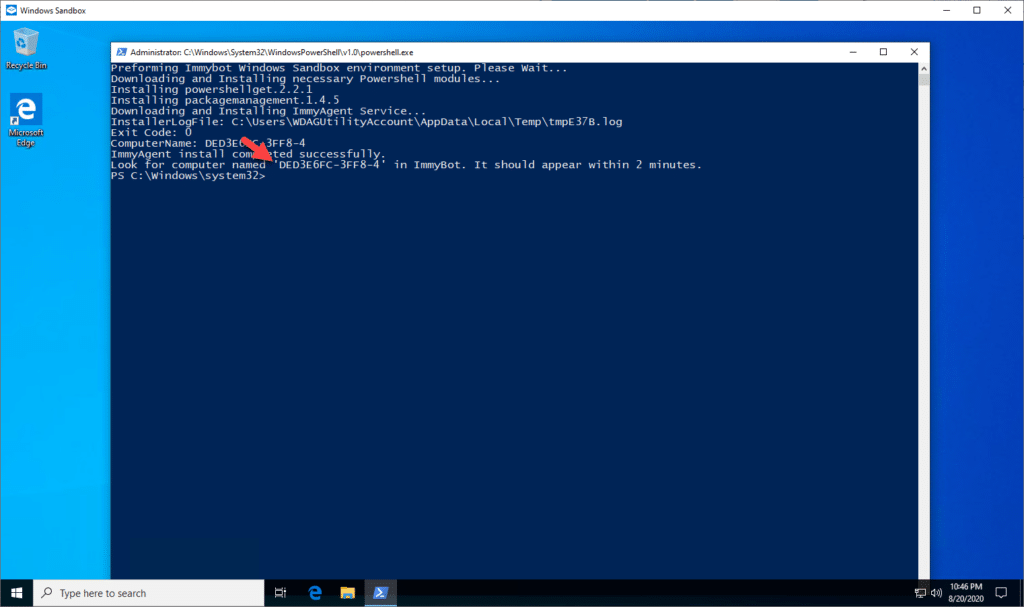
Step 3: Wait for ImmyBot Agent Installation
The ImmyBot Agent will automatically install in the Sandbox environment:
Step 4: Onboard the Sandbox Computer
Once the agent is installed, the computer will appear in ImmyBot. Onboard the Sandbox computer:
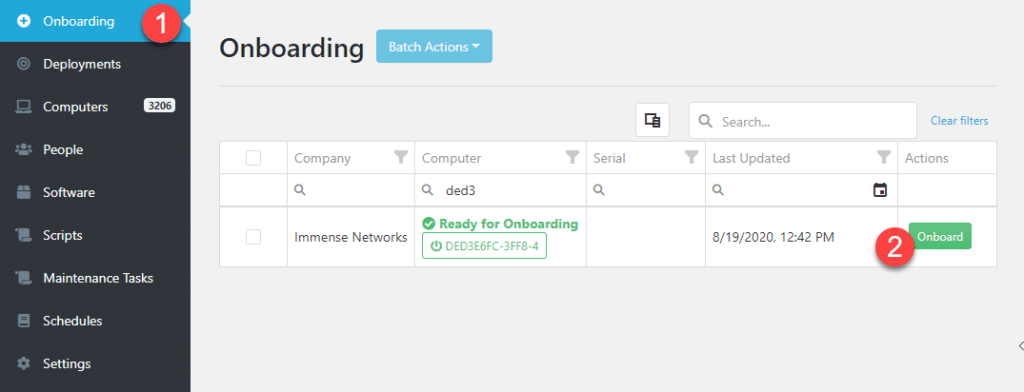
Step 5: Assign Customer and User
Select the appropriate customer and user for testing:
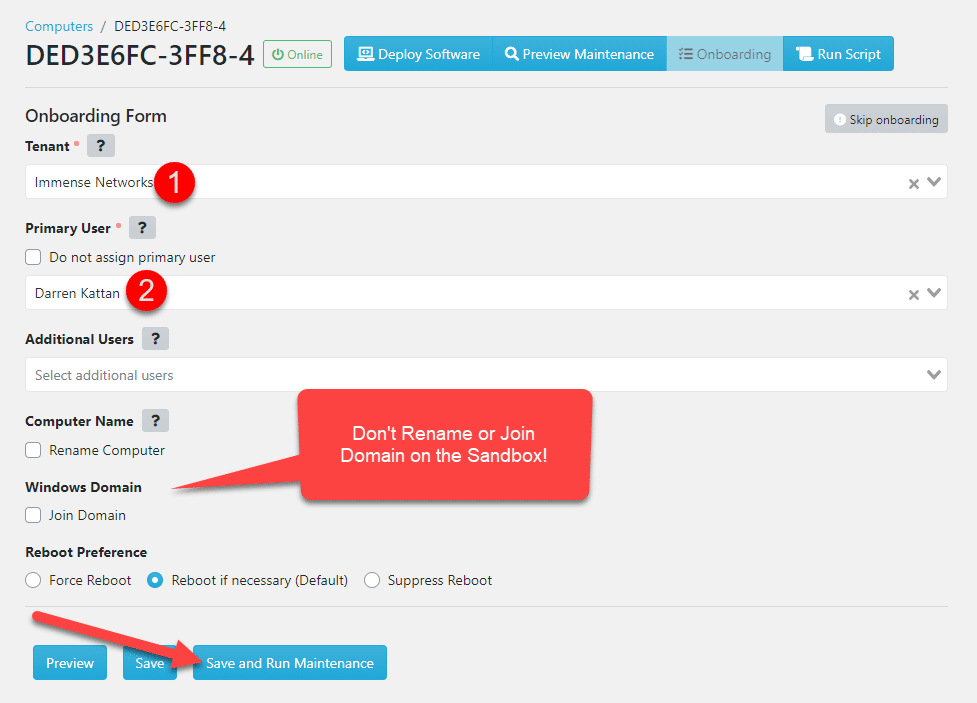
Step 6: Start the Onboarding Process
Begin the onboarding process to apply your deployments:
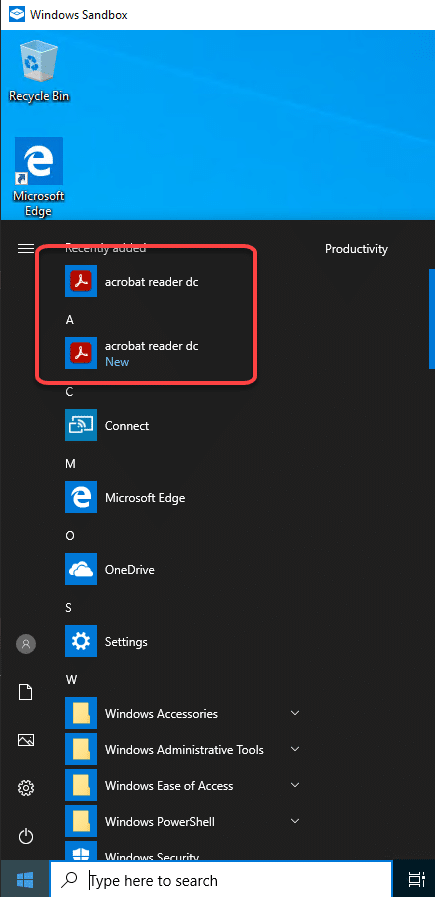
This will create an "Onboarding" maintenance session that will apply all applicable deployments to the Sandbox environment.
Limitations of Windows Sandbox
When testing with Windows Sandbox, be aware of these limitations:
- No Persistence: All changes are lost when the Sandbox is closed
- Driver Limitations: Software that requires drivers may not work properly
- Restart Limitations: Processes requiring restarts may not complete correctly
- Performance: Resource-intensive applications may run slower than on a physical machine
- Network Isolation: Some network-dependent features may behave differently
Best Practices for Testing
- Test One Thing at a Time: Focus on testing a single deployment or configuration
- Document Your Tests: Keep notes on what works and what doesn't
- Compare with Physical Machines: Verify critical deployments on physical machines after testing in Sandbox
- Use for Initial Validation: Sandbox is great for initial testing but may not catch all edge cases